Foram encontradas 60 questões.
Deseja-se projetar um circuito que acenda um led, com a sua máxima intensidade luminosa, com uma tensão contínua de !$ V_F !$= 15 V, conforme mostra o circuito a seguir:
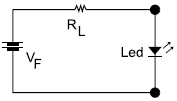
As especificações do led são: corrente para a máxima intensidade luminosa: 20 mA, tensão de operação: 2,2 V. Um resistor limitador RL que possa funcionar adequadamente, de valor e potência comercialmente disponíveis, e que permita que se utilize uma corrente próxima da máxima sem ultrapassá-la é:
Provas
Questão presente nas seguintes provas
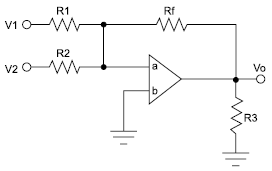
Deseja-se construir um circuito somador com um amplificador operacional ideal, no qual Rf = 2 k!$ \Omega !$.
Caso Vo = –2 V, V1 = 1 V e V2 = 2 V, tem-se que
Provas
Questão presente nas seguintes provas
No circuito a seguir, baseado em um amplificador operacional ideal, no qual R2 = 2 k!$ \Omega !$, foram efetuadas as seguintes medições: Vi = 1 V e Vo = 9 V. Para que esses valores pudessem ser obtidos, o valor de

Provas
Questão presente nas seguintes provas
O circuito a seguir possui um voltímetro e um amperímetro, ambos considerados ideais. R2 = 1 !$ \Omega !$ e R4 = 3 !$ \Omega !$.
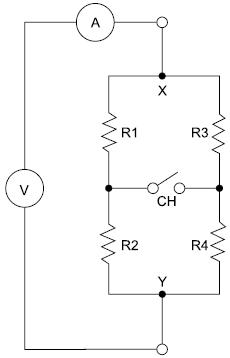
Foram efetuadas medições em duas condições:
• CH aberta: leitura do voltímetro = 6 V, leitura do amperímetro = 2 A.
• CH fechada: leitura do voltímetro = 6 V, leitura do amperímetro = 2 A.
Nessas condições, tem-se que
Provas
Questão presente nas seguintes provas
Deseja-se construir um circuito divisor de tensão com as seguintes características:
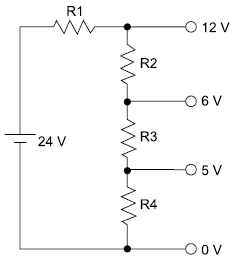
Sabendo-se que R2 = 150 !$ \Omega !$, tem-se que:
Provas
Questão presente nas seguintes provas
1. What is an analog-digital converter?
An Analog-Digital Converter (ADC) is a widely used electronic component that converts an analog electric signal (usually a voltage) into a digital representation. The ADCs are at the front-end of any digital circuit that needs to process signals coming from the exterior world. Its schematic symbol is:

The output of a microphone, the voltage at a photodiode or the signal of an accelerometer are examples of analog values that need to be converted so that a microprocessor can work with them.
2. How does the ADC convert a signal?
Many ways have been developed to convert an analog signal, each with its strengths and weaknesses. The choice of the ADC for a given application is usually defined by the requirements you have: if you need speed, use a fast ADC; if you need precision, use an accurate ADC; if you are constrained in space, use a compact ADC.
All ADCs work under the same principle: they need to convert a signal to a certain number of bits N. The sequence of bits represents the number and each bit has the double of the weight of the next, starting from the Most Significant Bit (MSB) up to the Least Significant Bit (LSB). In a nutshell, we want to find the sequence of bits bN−1, bN−2, ..., b0 that represents the analog value Vin as Vin=Σn=0N−1bn2nVref2N.
(www.onmyphd.com/?p=analog.digital.converter. Adaptado)
No trecho da resposta à segunda pergunta – In a nutshell, we want to find the sequence of bits…–, a expressão destacada equivale, em português, a
Provas
Questão presente nas seguintes provas
1. What is an analog-digital converter?
An Analog-Digital Converter (ADC) is a widely used electronic component that converts an analog electric signal (usually a voltage) into a digital representation. The ADCs are at the front-end of any digital circuit that needs to process signals coming from the exterior world. Its schematic symbol is:

The output of a microphone, the voltage at a photodiode or the signal of an accelerometer are examples of analog values that need to be converted so that a microprocessor can work with them.
2. How does the ADC convert a signal?
Many ways have been developed to convert an analog signal, each with its strengths and weaknesses. The choice of the ADC for a given application is usually defined by the requirements you have: if you need speed, use a fast ADC; if you need precision, use an accurate ADC; if you are constrained in space, use a compact ADC.
All ADCs work under the same principle: they need to convert a signal to a certain number of bits N. The sequence of bits represents the number and each bit has the double of the weight of the next, starting from the Most Significant Bit (MSB) up to the Least Significant Bit (LSB). In a nutshell, we want to find the sequence of bits bN−1, bN−2, ..., b0 that represents the analog value Vin as Vin=Σn=0N−1bn2nVref2N.
(www.onmyphd.com/?p=analog.digital.converter. Adaptado)
No trecho da resposta à segunda pergunta – Many wayshave been developed to convert an analog signal, each with its strengths and weaknesses. –, a expressão destacada pode ser substituída, sem alteração de sentido, por:
Provas
Questão presente nas seguintes provas
1. What is an analog-digital converter?
An Analog-Digital Converter (ADC) is a widely used electronic component that converts an analog electric signal (usually a voltage) into a digital representation. The ADCs are at the front-end of any digital circuit that needs to process signals coming from the exterior world. Its schematic symbol is:

The output of a microphone, the voltage at a photodiode or the signal of an accelerometer are examples of analog values that need to be converted so that a microprocessor can work with them.
2. How does the ADC convert a signal?
Many ways have been developed to convert an analog signal, each with its strengths and weaknesses. The choice of the ADC for a given application is usually defined by the requirements you have: if you need speed, use a fast ADC; if you need precision, use an accurate ADC; if you are constrained in space, use a compact ADC.
All ADCs work under the same principle: they need to convert a signal to a certain number of bits N. The sequence of bits represents the number and each bit has the double of the weight of the next, starting from the Most Significant Bit (MSB) up to the Least Significant Bit (LSB). In a nutshell, we want to find the sequence of bits bN−1, bN−2, ..., b0 that represents the analog value Vin as Vin=Σn=0N−1bn2nVref2N.
(www.onmyphd.com/?p=analog.digital.converter. Adaptado)
No trecho da resposta à primeira pergunta – ... that need to be converted so that a microprocessor can work with them. –, a expressão destacada indica
Provas
Questão presente nas seguintes provas
1. What is an analog-digital converter?
An Analog-Digital Converter (ADC) is a widely used electronic component that converts an analog electric signal (usually a voltage) into a digital representation. The ADCs are at the front-end of any digital circuit that needs to process signals coming from the exterior world. Its schematic symbol is:

The output of a microphone, the voltage at a photodiode or the signal of an accelerometer are examples of analog values that need to be converted so that a microprocessor can work with them.
2. How does the ADC convert a signal?
Many ways have been developed to convert an analog signal, each with its strengths and weaknesses. The choice of the ADC for a given application is usually defined by the requirements you have: if you need speed, use a fast ADC; if you need precision, use an accurate ADC; if you are constrained in space, use a compact ADC.
All ADCs work under the same principle: they need to convert a signal to a certain number of bits N. The sequence of bits represents the number and each bit has the double of the weight of the next, starting from the Most Significant Bit (MSB) up to the Least Significant Bit (LSB). In a nutshell, we want to find the sequence of bits bN−1, bN−2, ..., b0 that represents the analog value Vin as Vin=Σn=0N−1bn2nVref2N.
(www.onmyphd.com/?p=analog.digital.converter. Adaptado)
Na primeira resposta, um exemplo de valor analógico a ser convertido em valor digital é
Provas
Questão presente nas seguintes provas
1. What is an analog-digital converter?
An Analog-Digital Converter (ADC) is a widely used electronic component that converts an analog electric signal (usually a voltage) into a digital representation. The ADCs are at the front-end of any digital circuit that needs to process signals coming from the exterior world. Its schematic symbol is:

The output of a microphone, the voltage at a photodiode or the signal of an accelerometer are examples of analog values that need to be converted so that a microprocessor can work with them.
2. How does the ADC convert a signal?
Many ways have been developed to convert an analog signal, each with its strengths and weaknesses. The choice of the ADC for a given application is usually defined by the requirements you have: if you need speed, use a fast ADC; if you need precision, use an accurate ADC; if you are constrained in space, use a compact ADC.
All ADCs work under the same principle: they need to convert a signal to a certain number of bits N. The sequence of bits represents the number and each bit has the double of the weight of the next, starting from the Most Significant Bit (MSB) up to the Least Significant Bit (LSB). In a nutshell, we want to find the sequence of bits bN−1, bN−2, ..., b0 that represents the analog value Vin as Vin=Σn=0N−1bn2nVref2N.
(www.onmyphd.com/?p=analog.digital.converter. Adaptado)
According to the first answer, the Analog-Digital Converter
Provas
Questão presente nas seguintes provas
Cadernos
Caderno Container